 By Lindsay Townsend
By Lindsay TownsendFeasting for a noble or a king in the medieval period could be a splendid, lengthy, expensive affair, where dishes were produced and shown to display wealth and power. What about feasts for the bulk of the population who lived on the land?
In an age without freezers and only limited storage methods – smoking, salting, drying, preserving, keeping – all foodstuffs had to be produced in time to the rhythms of the farming year. In the Middle Ages, that meant the Christian calendar. Feasts were allied to the high points of harvests, saints’ days, Christ’s life, the change of the seasons and the winter and summer solstices.
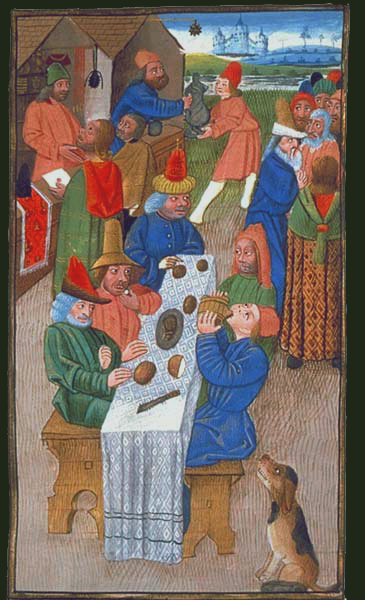 Christmas especially, covering the darkest time of the year and preceded by the fast of Advent, was celebrated for almost two weeks by all classes. No work was done in that ‘quiet’ season of the farming year and people celebrated by dancing, singing, story-telling, drinking and eating.
Christmas especially, covering the darkest time of the year and preceded by the fast of Advent, was celebrated for almost two weeks by all classes. No work was done in that ‘quiet’ season of the farming year and people celebrated by dancing, singing, story-telling, drinking and eating.In the countryside, some lucky peasants might be fed within their lords’ manor houses over Christmas as part of the Christian tradition of charity and share in rich dishes and strong beers. Other peasants would feast at home. Meat, as a luxury, would certainly be enjoyed, usually in the form of bacon, salted beef or mutton. Such cuts would be made into stews or slow roasted. Pepper was used as a spice by all classes and at Christmas carefully hoarded spices such as ginger, some dried herbs from the kitchen garden and perhaps even exotic fruits such as dried raisins might be added to the stews to add different flavours. We know that peasants had access to exotic spices and dried fruits because the Sumptuary Laws forbade indulgence in both rich clothes and expensive foods by the ‘lower’ classes.
Fine wheat bread, if peasants could produce it (by grinding the flour in secret away from their lords’ mill) would be a treat. River fish or eels would make a change from the usual salted dried cod of winter-time. Waterfowl, chickens, and – once they had escaped and bred from their specially constructed warrens – rabbits, could be caught, roasted or turned into stews and pies.
Hard cheese, which would keep through the winter, might have been part of a peasant’s Christmas feasting and certainly there would have been pottages, vegetable one pot stews made from the cut and come again greens and root vegetables (not potatoes yet) from the kitchen garden.
 As well as food treats, peasant households would decorate their homes for their Christmas feasts. Holly, ivy and mistletoe were cut and brought indoors to make the Christmas Bush that hung from the rafters. And after Christmas there was the festival of wassailing in cider apple districts. People would gather in the orchards and light fires under the trees, dance round them and drink to them.
As well as food treats, peasant households would decorate their homes for their Christmas feasts. Holly, ivy and mistletoe were cut and brought indoors to make the Christmas Bush that hung from the rafters. And after Christmas there was the festival of wassailing in cider apple districts. People would gather in the orchards and light fires under the trees, dance round them and drink to them.Richer peasants might feast on lamb or suckling pig, served with the first spring greens. Eggs featured heavily since they symbolised the stone rolled away from the tomb of Christ. Pace or paschal eggs, coloured with onion skins and wine, were part of the Easter feast, which, like Christmas, could last over several days.
(Pictures from Wikimedia Commons.)
Lindsay
http://www.lindsaytownsend.net
http://www.twitter.com/lindsayromantic